jdbc:sqlserver://172.16.1.114:52836;databaseName=celesta
jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/celesta
jdbc:oracle:thin:192.168.110.128:1521:XE
jdbc:derby://localhost:1527/corejava;create=trueCore Java. Lecture #8
JDBC API
@inponomarev
Ivan Ponomarev, Synthesized.io/MIPT
RDBMS — Relational Database Management Systems
Existed since the 1970s.
The most common way of storing information in a wide variety of systems.
A wide variety of mature, stable and feature-rich products: IBM DB2, Oracle, MS SQL Server, Postgres, etc. etc.
The SQL language is standardized and varies slightly from system to system.
In modern "big data" realities various NoSQL systems are being used for different tasks, but RDBMS is still the leader in prevalence
JDBC
"Java Database Connectivity"
Standard API for interaction with relational DBMS
Named after ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) for the C language developed by Microsoft
First version in 1996, current version is 4.3 (2017-09-21)
Actively used for decades
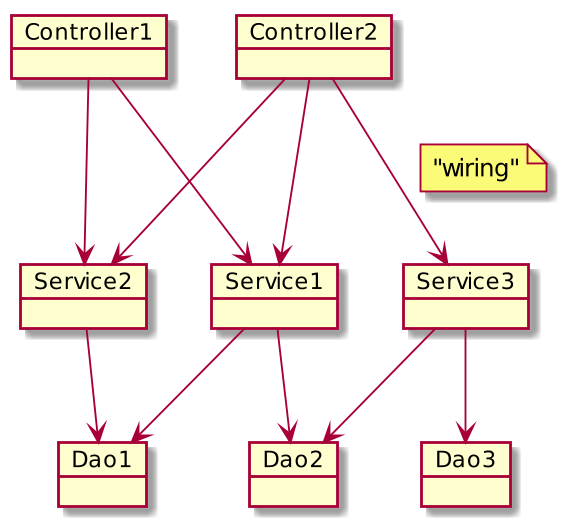
Application structure
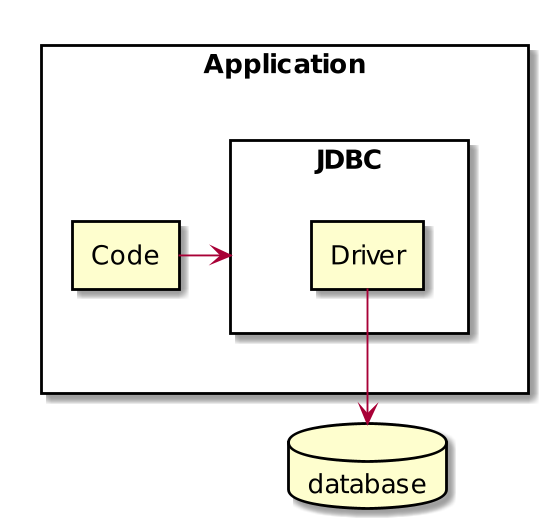
JDBC Drivers
Developed by database vendors or communities
Good databases have stable, high quality drivers
Connection Strings aka Database URLs
In a manner specific to each driver, specify the server, port, database and other connection parameters:
Creating Connection, Statement, getting ResultSet and iterating over it
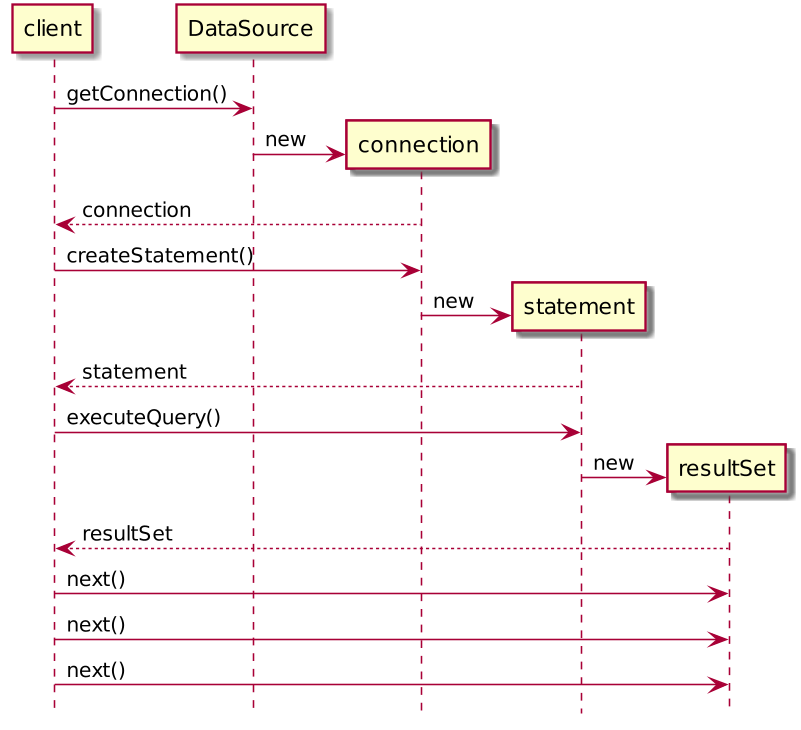
Getting the data and iteration
try (Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement()){
ResultSet result = stmt.executeQuery("select name from speaker");
while (result.next()) {
System.out.println(result.getString("name"));
}
}How to obtain JDBC Connection
What is written in many tutorials, and what you will never do in real life:
String connString = "jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/celesta"
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(connString);JDBC Connection features
Connection is a root object, "entry point" to all the interaction with the DBMS.
Created slowly (network connection with the DBMS, authorization, etc.).
Acquires resources: must be explicitly closed after use.
Tends to "spoil" (to "break" after some time).
Not thread-safe. Thread confinement is needed.
Workaround: connection pooling.
Connection Pool
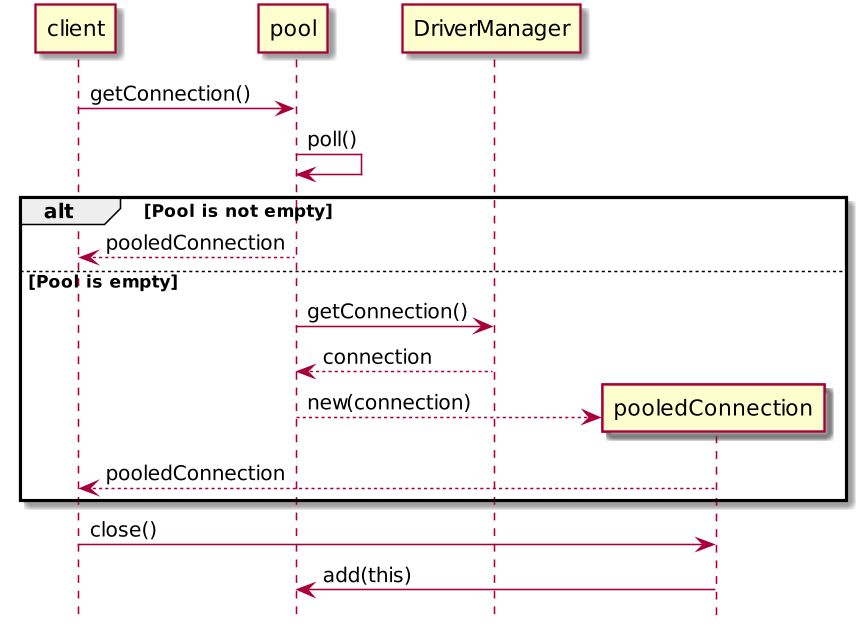
Connection Pool
Difficult to implement on your own competently
Provided by your framework / JDBC driver
There is
javax.sql.DataSourcewhich is a standard interface for Connection Pool.
DataSource connectionPool = ...
try (Connection conn = connectionPool.getConnection()) {
...
}Connection Pools (DataSource) implementations
Apache Commons DBCP
Hikari CP
Other frameworks or JDBC drivers (H2, for example)
Connection methods
transaction management
setAutoCommitcommitrollback
statements creation:
createStatement()— creates a generic object for passing SQL commandsprepareStatement(String sql)— creates a parameterized SQL command templateprepareCall(String sql)— creates a template for calling a stored procedure
Varieties of Statements
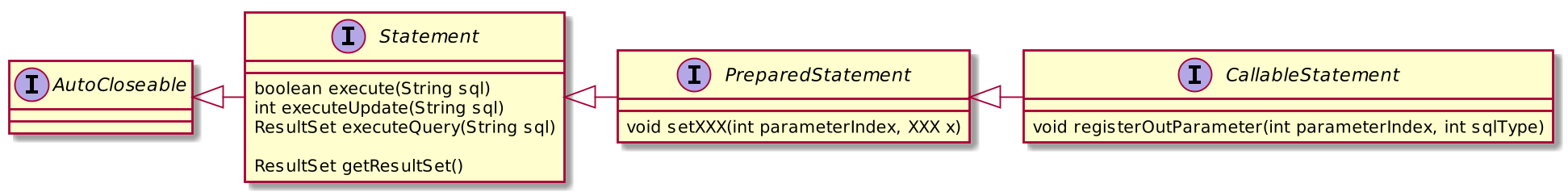
Statement and PreparedStatement
int confId = ...
try (PreparedStatement stmt =
conn.prepareStatement(
"select name from talk where conferenceid = ?")) {
//setting the parameter value
//we count parameters starting from one, not zero!!
stmt.setInt(1, confId);
ResultSet result = stmt.executeQuery();
while (result.next()) {
System.out.println(result.getString("name"));
}
}SQL Injection
Let’s remember once and for all: you cannot build queries to the database based on the input from the user
WRONG | CORRECT |
| |
SQL Injection
sql = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE name = '" + userName + "'"
userName = "' OR '1'='1"
userName = "a';DROP TABLE users;"
//... and many other nasty thingsSQL Injection

Demo example
Let’s write a database for talks at Java conferences
Main entities: at conferences there are speakers with their talks.
It happens that one talk is delivered with more than one speaker.
ER model
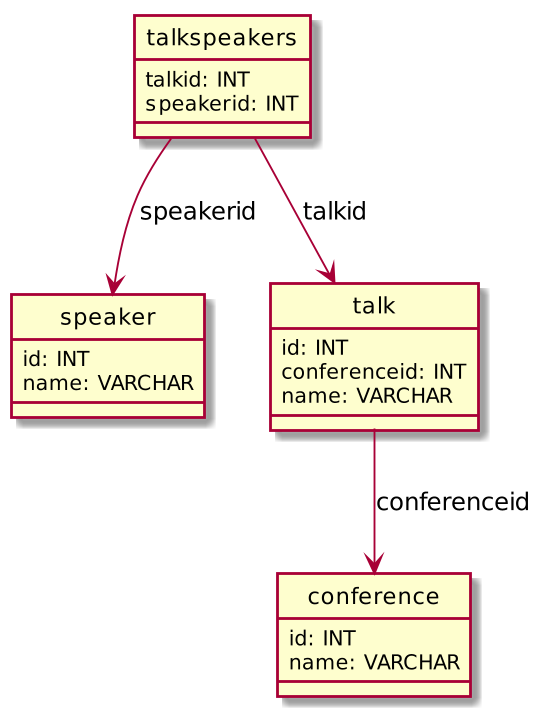
Our case study about talks and speakers
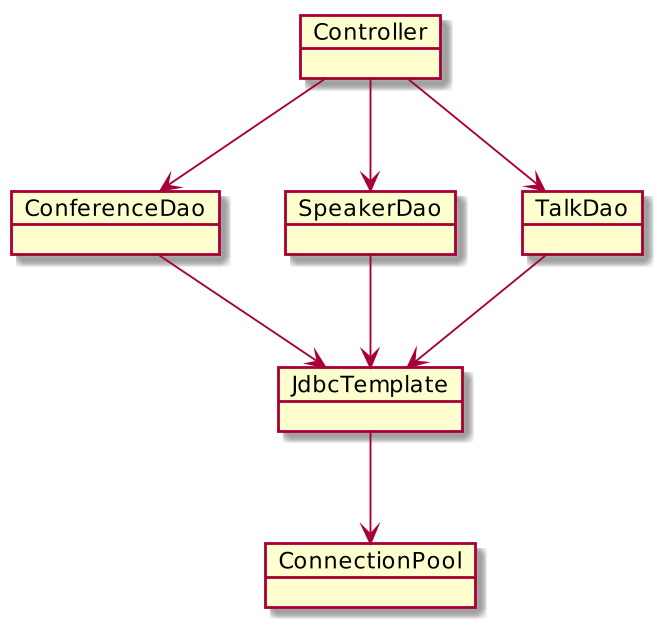
The real "layered" application architecture